|
coan 4.2.4
|
|
coan 4.2.4
|
|
Modules | |
| Macro-generated code | |
Files | |
| file | includes_tally.c |
| file | includes_tally.h |
Functions | |
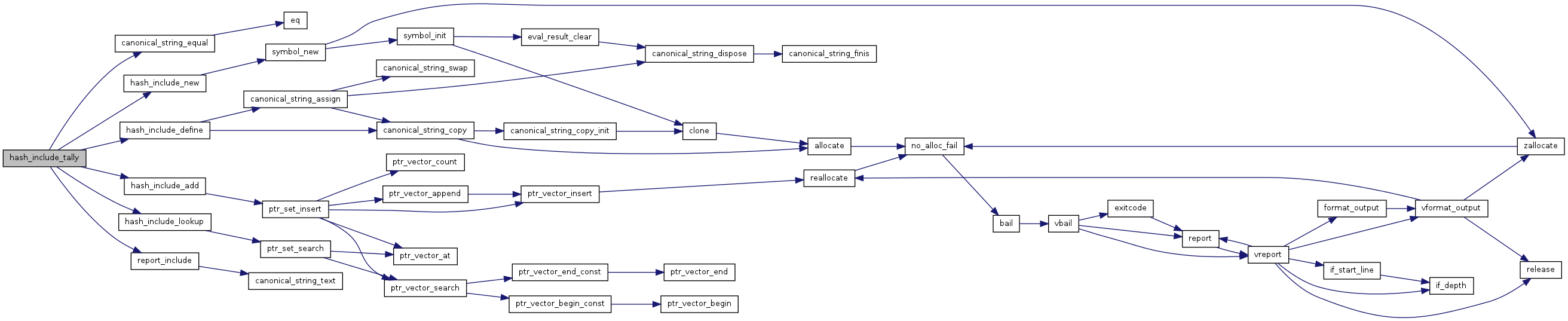
| void | hash_include_tally (char const *arg, size_t arglen, canonical_string_const_h sym_val) |
| void hash_include_tally | ( | char const * | arg, |
| size_t | arglen, | ||
| canonical_string_const_h | sym_val | ||
| ) |
Tally an occurrence of an hash-include argument.
| arg | The start of the hash-include argument. |
| arglen | The length of the hash-include argumentument. |
| sym_val | Where the hash-include argument is a defined symmbol, sym_def contains the canonicalised final value of that symbol, else NULL. |
If no hash-include argument matching arg exists in in the includes table, then a new hash-include argument is added to the table. If a matching hash-include argument is already in the table then that hash-include argument is given the definition sym_val if sym_val is not NULL and if the existing hash-include argument does not already have that definition. If sym_val is NULL then the matching hash-include argument is made undefined if it currently has a definition.
The occurrence of the hash-include argument is reported on stdout if the same hash-include argument has not already been seen or if --once is not in effect. If the hash-include argument is reported and sym_val is not NULL then the hash-include argument will be reported as a symbol that resolves sym_val.
Definition at line 110 of file includes_tally.c.
References canonical_string_equal(), GET_PUBLIC, hash_include_add(), hash_include_define(), hash_include_definition, hash_include_lookup(), hash_include_new(), hash_include_undefine, and report_include().
Referenced by eval_hash_include().